-
Article Review
-
Smelting and Recycling of Tantalum
탄탈럼의 제련과 리사이클링
-
Ho-Sang Sohn
손호상
- Global annual production of tantalum is only about 2,000 tons, yet it is an essential metal for modern industries and is considered …
전 세계 탄탈럼의 연간 생산량은 약 2,000 톤에 불과하지만, 현대 산업에 필수적인 금속으로 제한된 지역에서만 채굴되는 희소금속이다. Ta은 커패시터용의 금속 Ta 분말 …
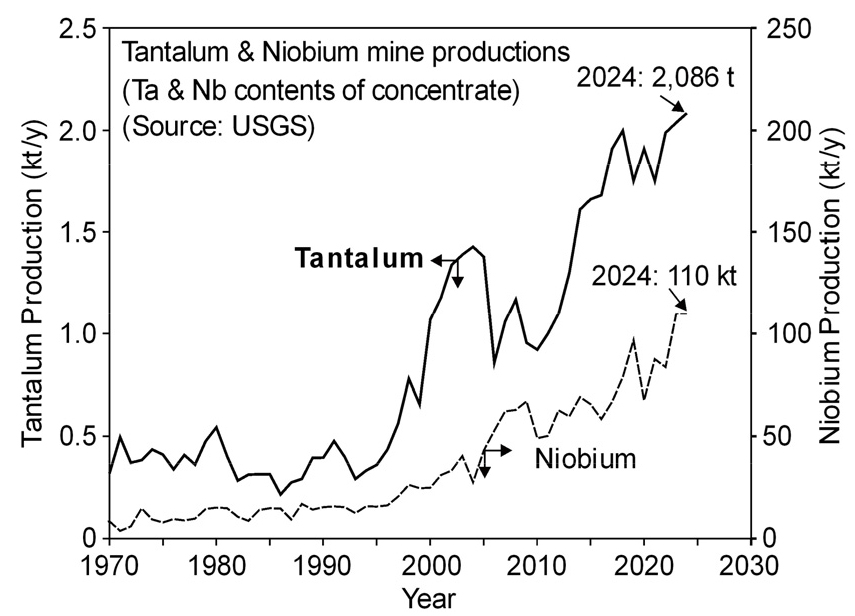
- Global annual production of tantalum is only about 2,000 tons, yet it is an essential metal for modern industries and is considered a rare metal because it is mined in only a few regions. Tantalum powder and wire for capacitors account for roughly 30% of global demand, and tantalum is also used in superalloys, chemical processing equipment, semiconductors, and other high-performance applications. Because tantalum commonly occurs together with columbite and tantalite, the ores must be processed to separate Ta2O5 and Nb2O5. The metal tantalum is produced by metallothermic reduction and molten-salt electrolysis of halides, as well as thermal reduction of oxides. Crude tantalum is refined into high-purity metal using high-temperature vacuum heat treatment or electron-beam melting. Bulk scrap, such as spent tantalum sputtering targets, is recovered through electron-beam melting and related processes. However, tantalum used as an alloying element is generally not separated and recovered on its own; instead, the alloy is remelted as is. Since a large portion of tantalum is used in capacitors, recycling has become an area of significant interest. In practice, the capacitors are first thermally decomposed, after which the tantalum is recovered by metallurgical processes.
- COLLAPSE
전 세계 탄탈럼의 연간 생산량은 약 2,000 톤에 불과하지만, 현대 산업에 필수적인 금속으로 제한된 지역에서만 채굴되는 희소금속이다. Ta은 커패시터용의 금속 Ta 분말 및 선재가 전 세계 수요의 약 30 %를 차지하며, 초합금, 화학장치, 반도체 등에도 사용된다. Ta은 탄탈라이트와 컬럼바이트에 공존하므로 Ta2O5와 Nb2O5로 분리하기 위해 광석을 분해하여야 한다. 금속 Ta은 할로겐화물의 금속열환원법과 용융염 전해법, 산화물의 열환원법 등으로 만들고 있다. 조금속 Ta은 고온의 진공 열처리나 전자빔 용융 정제법 등을 사용하여 고순도 Ta으로 만든다. Ta 폐타깃 등의 벌크 스크랩은 전자빔 용융 등으로 회수하지만, 합금원소로 첨가된 Ta은 별도로 회수하지 않으며, 원래의 합금 등으로 재용해한다. 또 Ta은 커패시터에 사용된 것이 많아 이의 리사이클링에 많은 관심이 주어져 있으나, 기본적으로는 커패시터를 열분해한 후 야금학적으로 Ta을 회수하고 있다.
-
Smelting and Recycling of Tantalum
-
Research Paper
-
Influence of Sieving Method of TiO2 Feed on the Production of Low-O Ti via Magnesiothermic Reduction in a Hydrogen Atmosphere
TiO2 원료 분급이 수소 분위기 내 마그네슘 열환원을 이용한 저산소 Ti 금속 분말 제조에 미치는 영향
-
Youngju Song, Sung-Hun Park, Jin-Ho Yoon, Jieun Lee, Jungshin Kang
송영주, 박성훈, 윤진호, 이지은, 강정신
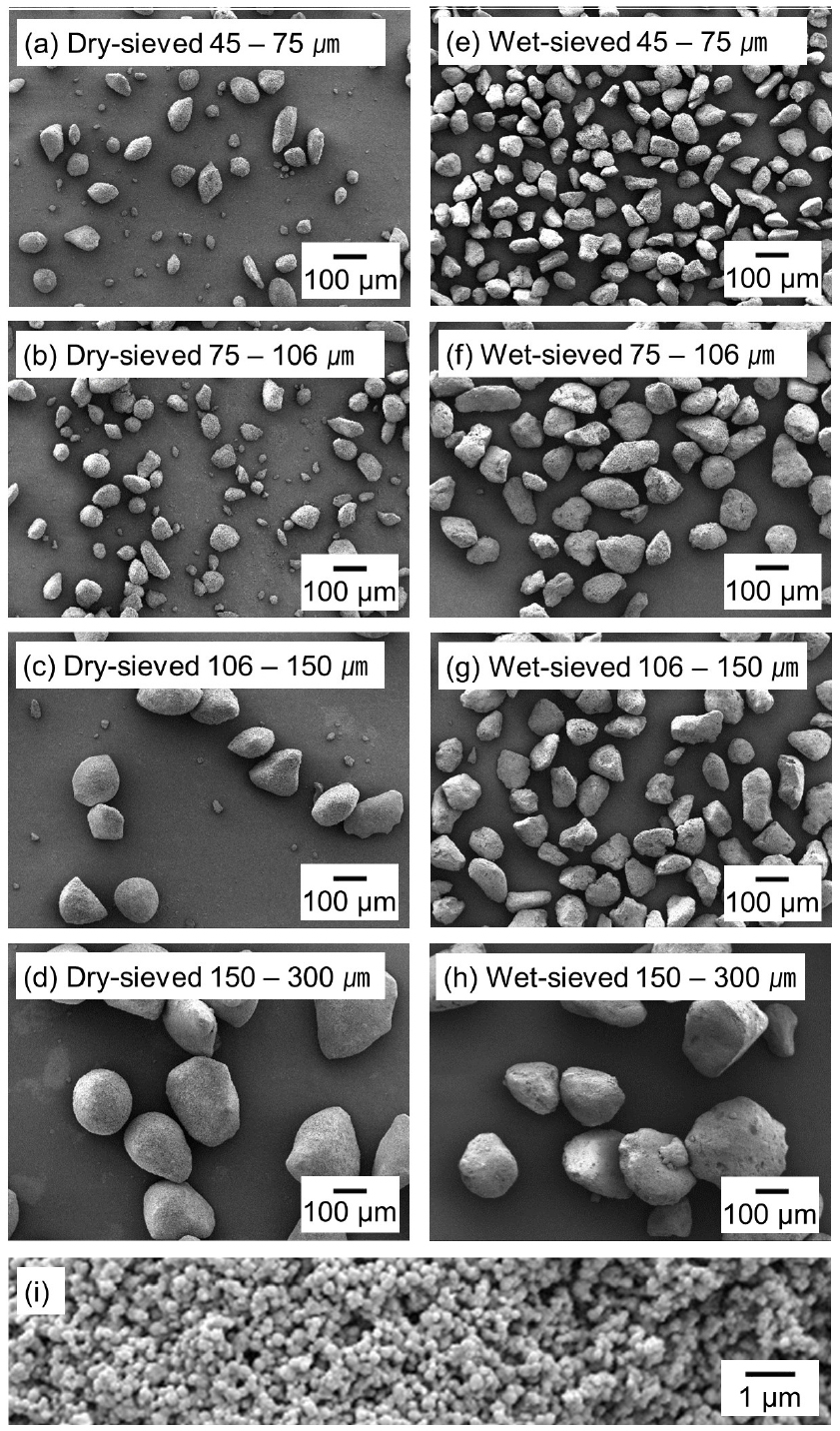
- In recent years, a novel method for producing titanium (Ti) with a low oxygen (O) concentration has been developed to overcome the …
최근 크롤(Kroll)법에 의한 타이타늄(Ti) 제조 시 문제점을 해결하고자 수소 가스(H2) 분위기에서 마그네슘(Mg) 금속을 이용한 이산화타이타늄(TiO2)의 열환원법에 의한 저산소 …
- In recent years, a novel method for producing titanium (Ti) with a low oxygen (O) concentration has been developed to overcome the limitations of the commercial Ti production process, the Kroll process. This method involves the reduction of titanium dioxide (TiO2) using magnesium (Mg) in a hydrogen gas (H2) atmosphere. In this study, the effects of the sieving method and the particle size of the TiO2 feed on the O concentration in the reduced Ti product were investigated, based on a thermodynamic analysis of the magnesiothermic reduction mechanism. Titanium hydride (TiH2) powder containing 0.415 – 0.480 mass%O was directly produced by reducing dry-sieved TiO2 feed, with a size range of 45 – 300 μm, using Mg under a 10 % H2 mixed gas atmosphere at 973 K. Furthermore, by comparing the magnesiothermic reduction results of wet-sieved TiO2 feed, the influence of the sieving method on the O concentration in the TiH2 product was evaluated.
- COLLAPSE
최근 크롤(Kroll)법에 의한 타이타늄(Ti) 제조 시 문제점을 해결하고자 수소 가스(H2) 분위기에서 마그네슘(Mg) 금속을 이용한 이산화타이타늄(TiO2)의 열환원법에 의한 저산소 Ti 제조법이 개발되고 있다. 본 연구에서는 TiO2 원료 분급방식 및 입도가 열환원 반응 후 생성된 Ti 산물의 산소 농도에 미치는 영향을 조사하였으며 환원 메커니즘에 대한 열역학적 분석을 실시하였다. 건식 체질을 통해 45 – 300 μm 입도 구간으로 분급된 TiO2 원료를 973 K의 10 % H2 혼합 가스 분위기에서 Mg 금속을 이용한 환원 시 0.415 – 0.480 mass%의 산소를 함유한 수소화타이타늄(TiH2) 분말이 제조되었다. 또한, 습식 체질을 통해 분급된 TiO2 원료 사용 시 환원 결과와의 비교를 통해, TiO2 원료의 분급법이 최종 TiH2 산물의 산소 농도에 미치는 영향을 평가하였다.

-
Influence of Sieving Method of TiO2 Feed on the Production of Low-O Ti via Magnesiothermic Reduction in a Hydrogen Atmosphere
-
Research Paper
-
Investigation on HCl Leaching of Ti Mixture Obtained by Deoxidation of Off-grade Ti Sponge Using Mg Metal
Mg을 이용한 Off-grade 타이타늄 스폰지 탈산 산물의 산 침출에 관한 연구
-
Hyunjin Na, Sung-Hun Park, Tae-Hyuk Lee, Jungshin Kang
나현진, 박성훈, 이태혁, 강정신
- To recycle off-grade Ti sponges, deoxidation using Mg in H2 gas has been recently developed. After deoxidation, acid leaching plays an …
최근, off-grade 타이타늄 (Ti) 스폰지의 재활용을 위해 수소 가스 (H2) 분위기에서 마그네슘 (Mg) 금속을 이용한 탈산 공정이 개발되고 있다. 탈산 …
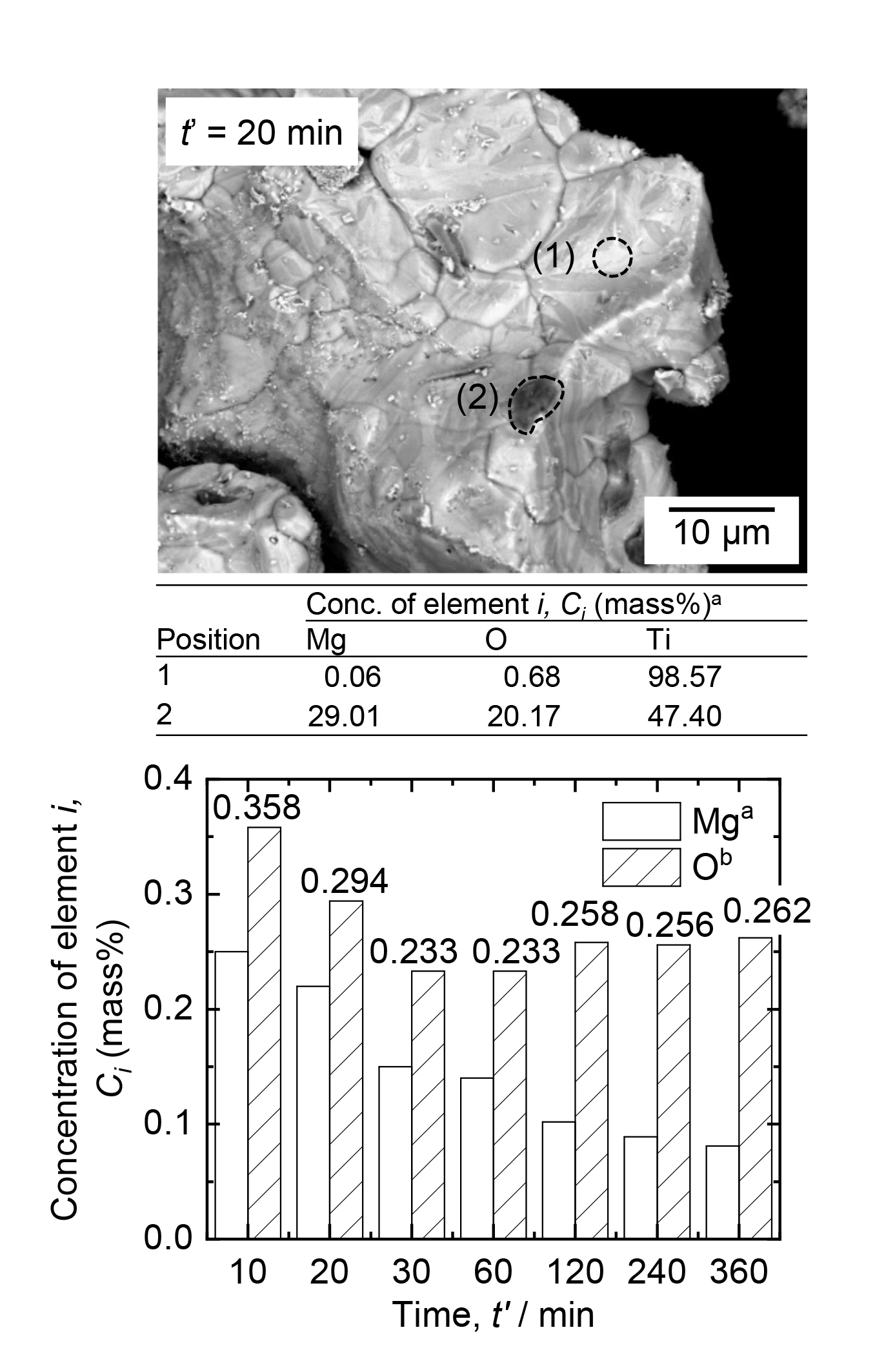
- To recycle off-grade Ti sponges, deoxidation using Mg in H2 gas has been recently developed. After deoxidation, acid leaching plays an important role in producing high-purity Ti without contamination by O. In this study, conditions for the HCl leaching of Ti mixtures obtained by deoxidation of an off-grade Ti sponge were optimized. The influences of leaching time, temperature, molarity of HCl solution, and bubbling gas on the O concentration in Ti were investigated, in addition to the dissolution behaviors of Mg, Ti, and Fe. When HCl leaching was conducted at 313 K under argon gas bubbling, the O concentration in Ti was 0.168 mass%, and the fractions of dissolved Ti and Fe were 1.01 % and 43.84 %, respectively. These results demonstrate the feasibility of mitigating O contamination in Ti with minimal Ti loss during the HCl leaching of a Ti mixture obtained after deoxidizing an off-grade Ti sponge.
- COLLAPSE
최근, off-grade 타이타늄 (Ti) 스폰지의 재활용을 위해 수소 가스 (H2) 분위기에서 마그네슘 (Mg) 금속을 이용한 탈산 공정이 개발되고 있다. 탈산 후 고순도의 Ti을 얻기 위해서는, 산 침출의 제어를 통한 산소 (O) 오염의 최소화가 중요하다. 본 연구에서는 off-grade Ti 스폰지를 수소 혼합 가스 분위기 중 Mg 금속으로 탈산하여 얻은 Ti 혼합물의 염산 (HCl)을 이용한 최적 침출 조건을 조사하였다. 특히, 침출 시간, 온도, HCl 용액의 몰농도 및 공급 가스의 종류가 Ti 내 O 농도와 Mg, Ti 및 철 (Fe)의 침출 거동에 미치는 영향을 조사하였다. 아르곤 (Ar) 가스를 버블링하며 313 K에서 HCl 침출을 수행한 결과, Ti 내 O 농도는 0.168 mass%였으며, Ti과 Fe의 침출률은 각각 1.01 %와 43.84 %를 나타냈다. 결과적으로, off-grade Ti 스폰지의 탈산 후 Ti 혼합물의 HCl 침출 최적화를 통해 Ti 손실 및 O에 의한 오염을 최소화하였고, 저산소 Ti의 회수가 가능함을 입증하였다.
-
Investigation on HCl Leaching of Ti Mixture Obtained by Deoxidation of Off-grade Ti Sponge Using Mg Metal
-
Research Paper
-
Burnability of High-Performance Cement Clinker Using KR Slag and Reduction Slag
KR슬래그와 환원슬래그를 사용한 고성능 시멘트 클링커의 소성 특성
-
Tae-hyung Kim, Young-jin Kim, Na-yeong Kim, Moon-Kwan Choi, WooCheol Jeong, Jin-sang Cho
김태형, 김영진, 김나영, 최문관, 정우철, 조진상
- In the cement industry, research on replacing the primary raw material, limestone, with non-carbonate industrial by-products is essential to reduce CO2 …
시멘트 산업은 CO2 배출량 감축을 위해 주원료인 석회석을 비탄산계 산업부산물로 대체하는 연구가 필수적이다. 본 연구에서는 제강 공정 부산물인 KR슬래그(Kambara Reactor slag)와 …
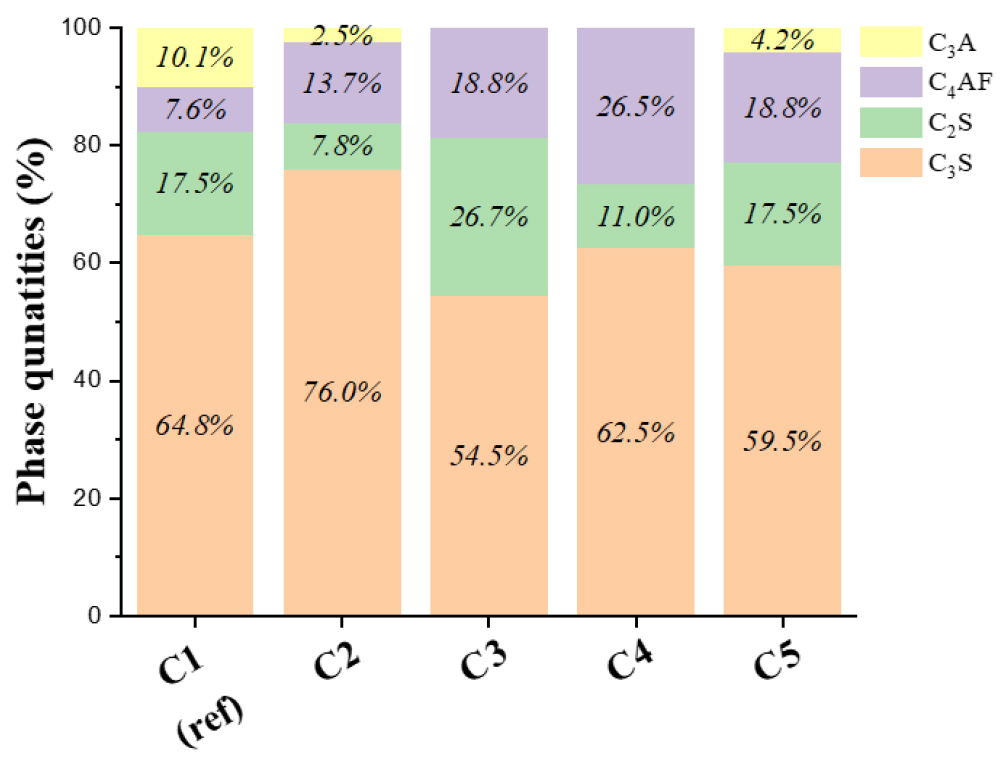
- In the cement industry, research on replacing the primary raw material, limestone, with non-carbonate industrial by-products is essential to reduce CO2 emissions. This study aims to manufacture high-performance cement clinker using a mixture of Kambara Reactor (KR) slag and reduction slag, which are by-products of the steelmaking process. A total of 5 types of clinker were sintered at 1,450℃, with the mixed slag substitution rate (0, 10, 15 wt. %) and Lime Saturation Factor (LSF: 100, 101) set as the main variables. The raw material characterization results demonstrated that the KR and reduction slags contained approximately 20~34 wt. % of belite (Dicalcium Silicate, C2S), an intermediate product in clinker phases, indicating their potential to shorten the alite (Tricalcium Silicate, C3S) formation reaction pathway. In particular, reduction slag containing 60 wt. % f Mayenite (Dodecacalcium hepta-aluminate, C12A7) as its main mineral phase, which was expected to promote the sintering process. A quantitative mineral phase analysis of the clinker revealed that 10 wt. % mixed slag substitution and an LSF of 100, the content of C3S, the main strength developing mineral, was 76.0 wt. %. This value was significantly higher than that of the reference clinker (C3S, 64.8 wt. %), which had no by-product substitution, confirming the potential for high performance. Furthermore, the TG/DSC analysis showed that the initial C3S formation temperature for the mixed slag condition was 1,206℃, which is up to 65℃ lower than that of the reference. This indicates that the use of mixed slag enhances burnability. This is attributed to the combined effects of C2S in the slag acting as a precursor to shorten the reaction pathway, and C12A7 in the reduction slag acting as a flux. This approach, offers the advantage of simultaneously achieving high performance and enhanced burnability and, presents a novel pathway for the development of low-carbon, high-performance cement.
- COLLAPSE
시멘트 산업은 CO2 배출량 감축을 위해 주원료인 석회석을 비탄산계 산업부산물로 대체하는 연구가 필수적이다. 본 연구에서는 제강 공정 부산물인 KR슬래그(Kambara Reactor slag)와 환원슬래그를 혼합 사용하여 고성능 시멘트 클링커를 제조하고자 하였다. 혼합슬래그 대체율(0, 10, 15 wt. %)과 석회포화비(LSF: 100, 101)를 주요 변수로 설정하여 총 5종의 클링커를 1,450℃에서 소성하였다. 원료 특성 분석 결과, 사용된 KR슬래그와 환원슬래그는 시멘트 광물상의 중간 생성물인 벨라이트(Dicalcium Silicate, C2S)를 약 20~34 wt. % 함유하여 알라이트(Tricalcium Silicate, C3S) 생성 반응 경로를 단축시킬 수 있는 잠재력을 보였다. 특히 환원슬래그는 주 광물상으로 Mayenite(Dodecacalcium hepta-aluminate, C12A7)를 60 wt. % 이상 함유하고 있어 소성 반응 촉진이 기대되었다. 클링커의 광물상 정량분석 결과, 혼합슬래그를 10 wt. % 대체하고 LSF를 100으로 설계한 조건에서 주 강도 발현 광물인 C3S 함량이 76.0 wt. %로 산업부산물 대체율이 적용되지 않은 대조군 클링커(C3S, 64.8 wt. %) 대비 월등히 높게 나타나 고성능화 가능성을 확인하였다. 또한, TG/DSC 분석 결과 혼합슬래그를 사용한 조건에서 C3S 생성 초기 피크 온도가 기준 대비 최대 65℃ 낮은 1,206℃로 확인되어, 슬래그 혼합 사용이 클링커의 소성 특성을 개선함을 입증하였다. 이는 슬래그에 포함된 C2S가 전구물질로 작용하여 반응 경로 단축, 환원슬래그 내 C12A7의 융제(flux) 역할이 복합적으로 작용한 결과로, 고성능화와 소성 특성 향상을 동시에 달성할 수 있는 이점을 통해 저탄소 고성능 시멘트 개발의 새로운 경로를 제시한다.
-
Burnability of High-Performance Cement Clinker Using KR Slag and Reduction Slag
-
Research Paper
-
A Study on the Leaching Behavior of Li, Fe and P from Lithium Iron Phosphate Cathode Powder Using Deep Eutectic Solvents
심층 공융 용매를 사용하여 리튬인산철 양극재 분말로부터 리튬, 철 그리고 인 성분의 침출 거동에 관한 연구
-
Hee-Seon Kim, SeongWon Kim, Dae-Weon Kim
김희선, 김성원, 김대원
- With the increasing global demand for electric vehicles, the end-of-life battery market is rapidly expanding. Consequently, the separation and recovery of valuable …
전 세계적으로 전기차의 수요가 증가함에 따라 사용 후 배터리 시장 규모 또한 확대되고 있다. 이에 사용 후 배터리로부터 유가 자원을 분리 및 …
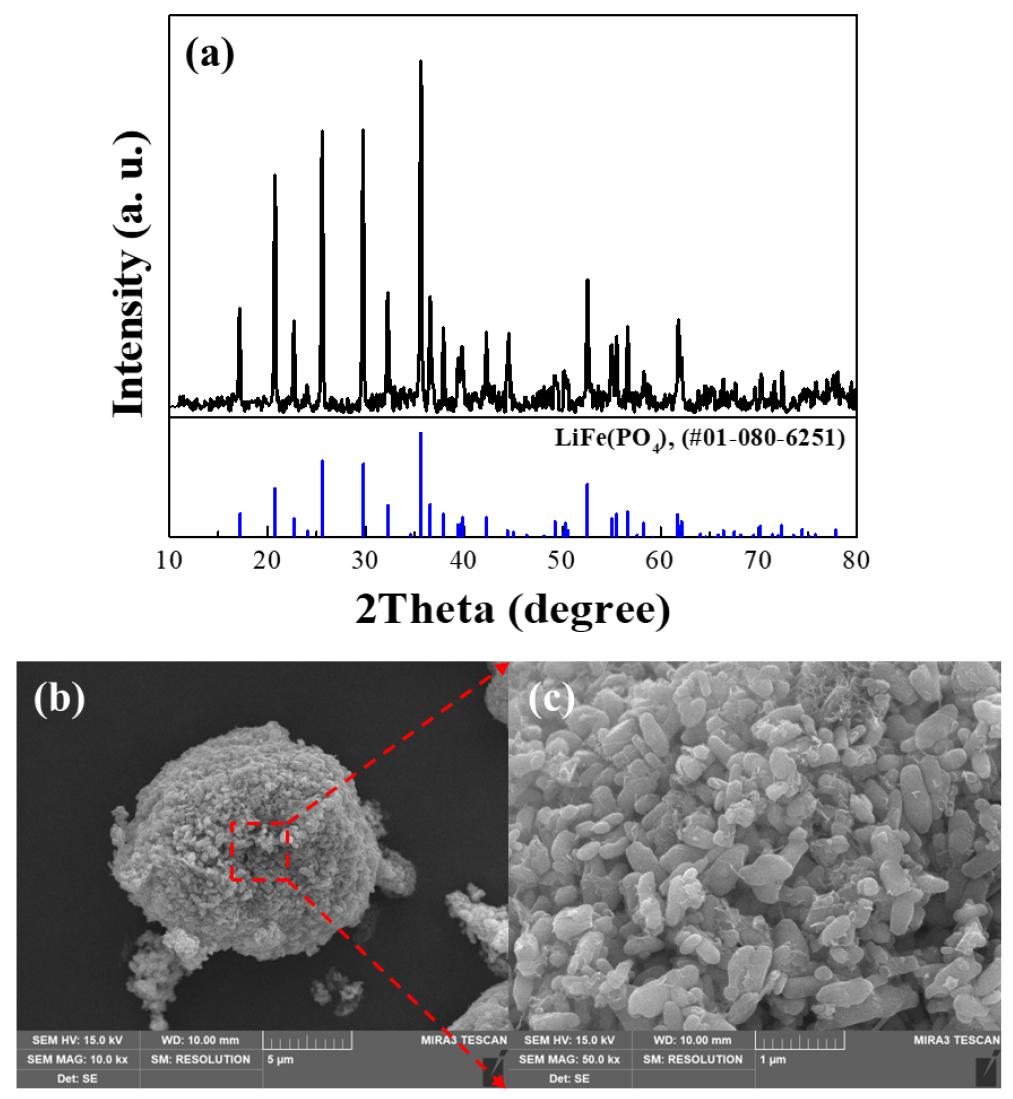
- With the increasing global demand for electric vehicles, the end-of-life battery market is rapidly expanding. Consequently, the separation and recovery of valuable resources from spent batteries have attracted increasing interest. Conventional hydrometallurgical recycling processes often cause environmental pollution; hence, environmentally benign processes utilizing green solvents have recently garnered significant attention. In this study, the leaching behaviors of the major elements in lithium iron phosphate cathode powder were investigated using deep eutectic solvents (DESs), which are emerging as eco-friendly alternatives. As comparative studies on various DESs using the same LFP feedstock are limited, five different DESs were evaluated in this work. Based on the experimental results, an optimal DES was selected, and selective leaching of lithium was achieved by optimizing the additives and reaction times. Inductively coupled plasma–optical emission spectrometry analysis indicated a lithium leaching efficiency of approximately 91% for choline chloride–ethylene glycol-based DES combined with K2S2O8 as an oxidizing additive. In addition, phosphorus leaching was suppressed to approximately 3%, and iron was not leached, indicating a high lithium recovery efficiency and superior selectivity. Finally, the feasibility of selective lithium leaching using DESs as environmentally benign solvents was confirmed.
- COLLAPSE
전 세계적으로 전기차의 수요가 증가함에 따라 사용 후 배터리 시장 규모 또한 확대되고 있다. 이에 사용 후 배터리로부터 유가 자원을 분리 및 회수하는 연구에 관한 관심이 증가하고 있다. 그중 기존 습식제련 재활용 공정은 환경오염 문제를 야기할 수 있어, 최근 친환경 용매를 이용한 환경 저부담 공정이 주목받고 있다. 이에 본 연구에서는 친환경 용매로 주목받고 있는 심층 공융 용매(Deep Eutectic Solvent, DES)를 활용하여 침출 용매에 따른 LFP 양극재 분말 내 주요 원소들의 침출 거동을 확인하였다. 주요 원소들의 침출 거동 확인 후 리튬 성분의 선택적 침출을 위하여 첨가제 및 반응시간을 공정 변수로 하여 침출 실험을 진행하였다. 공정별 침출액의 ICP-OES 분석을 통해 침출율 및 분리 효율을 비교한 결과 ChCl-EG 기반의 DES를 활용하여 K2S2O8 산화제를 첨가제로 투입하였을 때의 조건에서 리튬 성분의 침출율은 약 91%, 인 성분은 약 3% 그리고 철 성분은 침출되지 않아 높은 리튬 침출율과 높은 선택도임을 확인할 수 있었다.
-
A Study on the Leaching Behavior of Li, Fe and P from Lithium Iron Phosphate Cathode Powder Using Deep Eutectic Solvents
-
Research Paper
-
Fundamental Study on the Separation Characteristics of Cathode, Anode, and Lithium from Black Mass with the NMC Reduction in Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries
사용 후 배터리의 양극재 환원 반응에 따른 블랙매스 양극재와 음극재 및 리튬의 분리·선별 특성 기초 연구
-
Chanwoo Yang, Kwangsuk You, Kwanho Kim, Gilsang Hong
양찬우, 유광석, 김관호, 홍길상
- In the recycling of spent lithium-ion batteries, the pretreatment process for recovering black mass generally consists of crushing and grinding, heat treatment …
사용 후 배터리로부터 블랙매스를 회수하는 전처리 공정은 일반적으로 파·분쇄 공정, 유기물 제거를 위한 열처리 공정, 그리고 불순물 제거를 위한 선별·분급 공정으로 구성된다. …
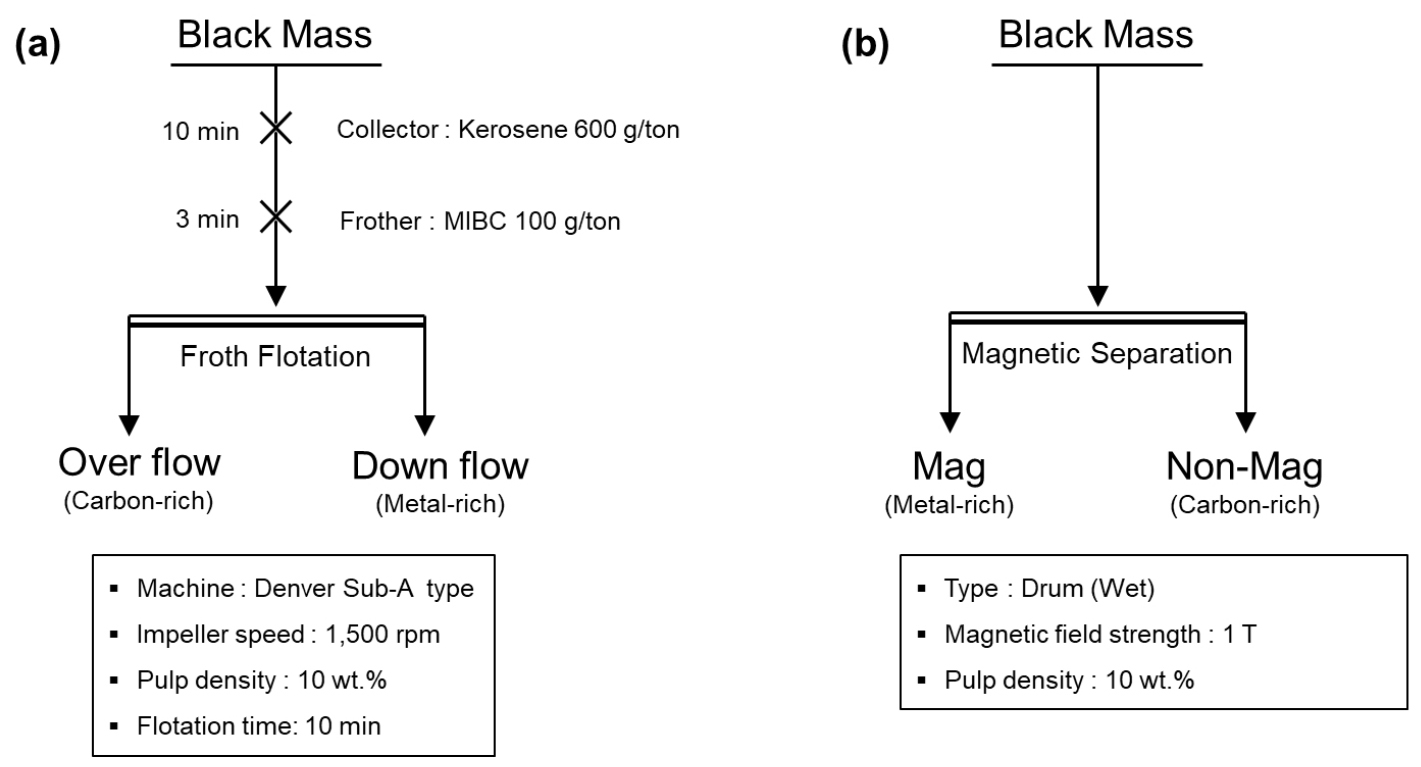
- In the recycling of spent lithium-ion batteries, the pretreatment process for recovering black mass generally consists of crushing and grinding, heat treatment to remove organic materials, and separation and classification to remove impurities. During heat treatment, depending on the heating temperature, the removal of organics, cathode reduction and lithium phase transformation can occur simultaneously. Therefore, this study discusses the fundamental separation characteristics of the cathode, anode, and lithium in a black mass associated with phase changes at the cathode reduction temperature. For this purpose, black mass was heat-treated at 550 ℃ for 2h under an N2 atmosphere, and the flotation and magnetic separation characteristics of the cathode and anode materials, as well as lithium leaching characteristics in aqueous solution, were examined. The results confirmed the removal of organics and the reduction of the cathode material. Compared to untreated black mass, the separation efficiency increased by approximately 43.9% in flotation and 69.3% in magnetic separation. In addition, aqueous leaching tests demonstrated that approximately 76.4% of the Li in the black mass was leached. These findings indicate that reductive heat treatment can significantly enhance the separation efficiency between the cathode and anode while enabling lithium recovery in the aqueous phase. The results of this study are expected to serve as fundamental data for developing optimal processes for separating the cathode, anode, and lithium from black mass under various heat-treatment conditions.
- COLLAPSE
사용 후 배터리로부터 블랙매스를 회수하는 전처리 공정은 일반적으로 파·분쇄 공정, 유기물 제거를 위한 열처리 공정, 그리고 불순물 제거를 위한 선별·분급 공정으로 구성된다. 이 중 열처리 단계에서는 가열 온도에 따라 유기물 제거뿐 아니라 양극재의 환원 반응과 리튬의 상 전환 반응이 동시에 일어난다. 이에 본 연구에서는 블랙매스 내 양극재의 환원 반응 온도에서 양극재와 음극재, 그리고 리튬의 상변화에 따른 분리·선별 기초 특성을 논하고자 한다. 이를 위해 본 연구에서는 질소 분위기 550 ℃에서 2시간 열처리한 블랙매스를 대상으로 양극재–음극재의 부유선별 및 자력선별 특성과 리튬의 수용액 용출 특성을 검토하였다. 실험 결과, 열처리를 통해 유기물 제거와 양극재의 환원 반응이 확인되었으며, 열처리를 하지 않은 블랙매스 대비 부유선별 및 자력선별의 선별효율이 각각 약 43.9%, 약 69.3% 증가하였다. 또한 용출 실험에서 블랙매스 내 리튬의 약 76.4%가 용출되었다. 즉, 환원 열처리는 양극재–음극재의 선별효율을 유의미하게 향상시키는 동시에 리튬의 수용액 회수를 가능하게 함을 시사한다. 본 연구에서 도출된 결과는 향후 열처리 조건에 따른 블랙매스의 양극재-음극재 및 리튬의 최적 분리·선별 공정 개발을 위한 핵심 기초 자료로 활용될 수 있을 것이다.
-
Fundamental Study on the Separation Characteristics of Cathode, Anode, and Lithium from Black Mass with the NMC Reduction in Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries
-
Research Paper
-
Influence of Slag Composition and Viscosity on Diameter of Slag Wool Using Dimensional Analysis-Based Double-Spinning Model
차원 해석 기반 더블 스피닝 모델을 활용한 슬래그울 직경에 대한 배합 조성 및 점도의 영향
-
Eun-Jin Jung, Sun-Joong Kim
정은진, 김선중
- The present study implemented a proposed double-disc spinning model based on dimensional analysis to predict fiber diameters of mineral wool. The reliability …
본 연구에서는 차원해석에 기반한 더블 스핀 모델을 구현하여 미네랄울의 섬유 직경을 예측하는 방법을 제시하였다. 현무암, 슬래그, 광석 등 다양한 원료로 제조된 19개 …
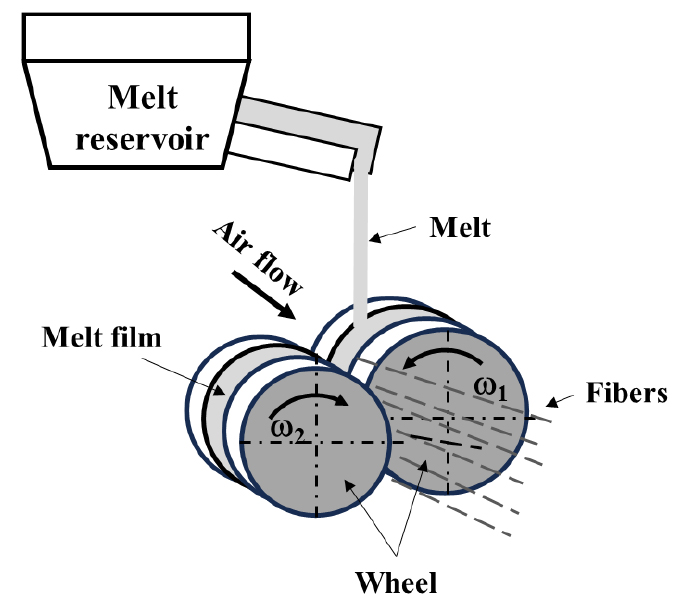
- The present study implemented a proposed double-disc spinning model based on dimensional analysis to predict fiber diameters of mineral wool. The reliability of the model was validated using fiber diameter data from 19 different mineral wool compositions manufactured from various raw materials including basalt, slag, and stone. Viscosity measurements of synthesized slag were experimentally conducted at 1773 K using Pt-Rh crucibles, and comparison with FactSage calculations showed good agreement for slag containing FeO. Model calculations revealed that when the melt viscosity was larger than approximately 15 Pa·s, measured and calculated fiber diameters showed similar values; however, the deviation between the two diameters increased with increasing viscosity. By optimizing composition of synthesized slag to adjust melt viscosity to approximately 1.5 Pa·s, it was predicted that fiber diameters of approximately 6 μm could be achieved. The results of this study are expected to serve as an important parameter for composition design in the manufacture of high-quality slag wool.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구에서는 차원해석에 기반한 더블 스핀 모델을 구현하여 미네랄울의 섬유 직경을 예측하는 방법을 제시하였다. 현무암, 슬래그, 광석 등 다양한 원료로 제조된 19개 미네랄울 조성의 섬유 직경 데이터를 활용하여 모델의 신뢰성을 검증하였다. 실험적으로 Pt-Rh 도가니를 이용하여 1773 K에서 인조 슬래그의 점도를 측정하였으며, FactSage 계산값과의 비교를 통해 FeO 함유 슬래그에서 거의 일치함을 확인하였다. 모델 계산 결과, 용융물 점도가 약 15 Pa·s 이하일 때 섬유 직경의 측정값과 계산값이 유사한 경향을 보였으나, 점도가 높아질수록 편차가 증가하는 것을 확인하였다. 인조 슬래그의 최적 배합을 통해 용융물 점도를 약 1.5 Pa·s로 조정할 경우 섬유 직경이 약 6 μm까지 도달 가능함을 예측하였다. 본 연구의 결과는 고품질 슬래그울 제조를 위한 배합 설계의 중요한 지표로 활용될 수 있을 것으로 판단된다.
-
Influence of Slag Composition and Viscosity on Diameter of Slag Wool Using Dimensional Analysis-Based Double-Spinning Model
-
Research Paper
-
Recovery of Lithium Hydroxide Solution from Lithium Sulfate Solution Using Bipolar Electrodialysis
양극성 전기투석을 이용한 황산리튬용액으로부터 수산화리튬용액의 회수
-
Jeeyoung Park, Woojin Seo, Youbeen Park, Sumin Lee, Kyoungkeun Yoo
박지영, 서우진, 박유빈, 이수민, 유경근
- This study investigated the feasibility of directly recovering lithium hydroxide and sulfuric acid from lithium sulfate solutions using a bipolar electrodialysis (BPED) …
본 연구는 양극성 전기투석(BPED) 시스템을 이용하여 황산리튬 용액으로부터 수산화리튬과 황산을 직접 회수하는 공정의 가능성을 평가하였다. 실험은 인가전압(15-30 V), 원료용액 부피, 리튬 초기농도의 …
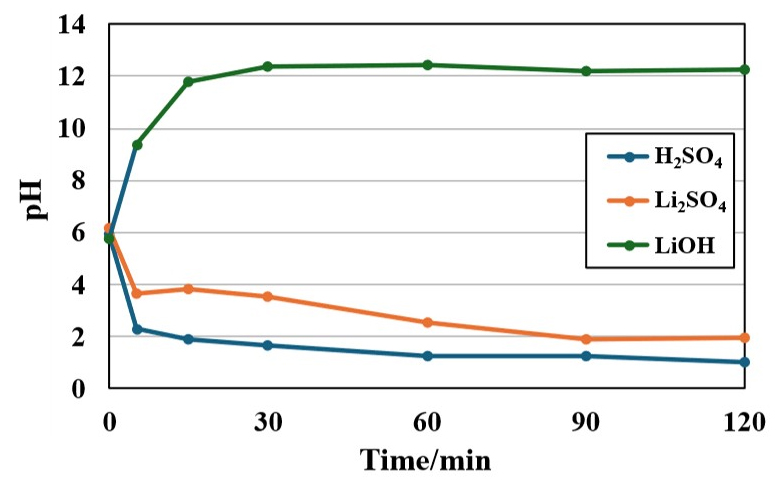
- This study investigated the feasibility of directly recovering lithium hydroxide and sulfuric acid from lithium sulfate solutions using a bipolar electrodialysis (BPED) system. Experiments were conducted by varying process conditions including applied voltage (15-30 V), feed solution volume, and initial lithium concentration. When the applied voltage increased from 15 V to 30 V, conversion time was shortened from 5 hours to 90 minutes while maintaining similar final conversion ratios of 74-76 %. At 20 V for 2 hours, optimal conversion ratio of 74.8 % for lithium and 70.2 % for sulfur were achieved. The increases in feed solution volume or initial lithium concentration enhanced recovered lithium concentration, but conversion ratios remained constant at approximately 75 %, where pH measurements confirmed successful generation of lithium hydroxide (pH 12) in the basic recovery tank and sulfuric acid (pH 1) in the acidic recovery tank. These results indicate that BPED systems are a promising technology for simultaneous recovery of lithium hydroxide and sulfuric acid from lithium sulfate solutions.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구는 양극성 전기투석(BPED) 시스템을 이용하여 황산리튬 용액으로부터 수산화리튬과 황산을 직접 회수하는 공정의 가능성을 평가하였다. 실험은 인가전압(15-30 V), 원료용액 부피, 리튬 초기농도의 공정 조건을 변화시키며 수행되었다. 인가전압이 15 V에서 30 V로 증가할 때 전환 시간은 5시간에서 90분으로 단축되나 최종 전환율은 74-76 %로 유사하게 나타났으며, 20 V 조건에서 2시간 처리 시 리튬과 황의 전환율이 각각 74.8 %와 70.2 %로 최적 결과를 나타냈다. 원료용액 부피 증가 또는 리튬 초기농도 증가 시 회수되는 리튬 농도는 증가하나 전환율은 약 75 %로 일정하게 유지되었으며, 이 과정에서 pH 측정 결과 염기회수탱크는 pH 12, 산회수탱크는 pH 1로 수산화리튬과 황산의 성공적인 생성을 확인하였다. 이 결과로부터 BPED 시스템을 이용할 때 황산리튬으로부터 수산화리튬과 황산을 동시에 회수가 가능하다고 판단되었다.
-
Recovery of Lithium Hydroxide Solution from Lithium Sulfate Solution Using Bipolar Electrodialysis
-
Corrigendum
-
Corrigendum to : Analysis of Electrolyte Recycling Technology from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries(LIBs)
Corrigendum to : 폐 리튬이온전지(LIB) 전해액 재활용 기술 분석
-
Jaewoo Ahn, Junhee Kim, Jaehyuk Chang, Minhyuk Seo, Youngjae Lee
안재우, 김준희, 장재혁, 서민혁, 이영재
-
Corrigendum to : Analysis of Electrolyte Recycling Technology from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries(LIBs)



 Resources Recycling
Resources Recycling








