-
Article Review
-
Smelting and Recycling of Hafnium
하프늄의 제련과 리사이클링
-
Ho-Sang Sohn
손호상
- Hafnium (Hf) is a rare metal that is essential for advanced industries such as nuclear power, superalloys, and semiconductors. This paper reviews …
하프늄은 원자력, 초합금, 반도체 등의 첨단산업에 필수적인 희소금속이다. 본 논문에서는 이러한 Hf의 생산량과 용도 및 제련 기술 등에 관하여 고찰하였다. Hf의 전 …
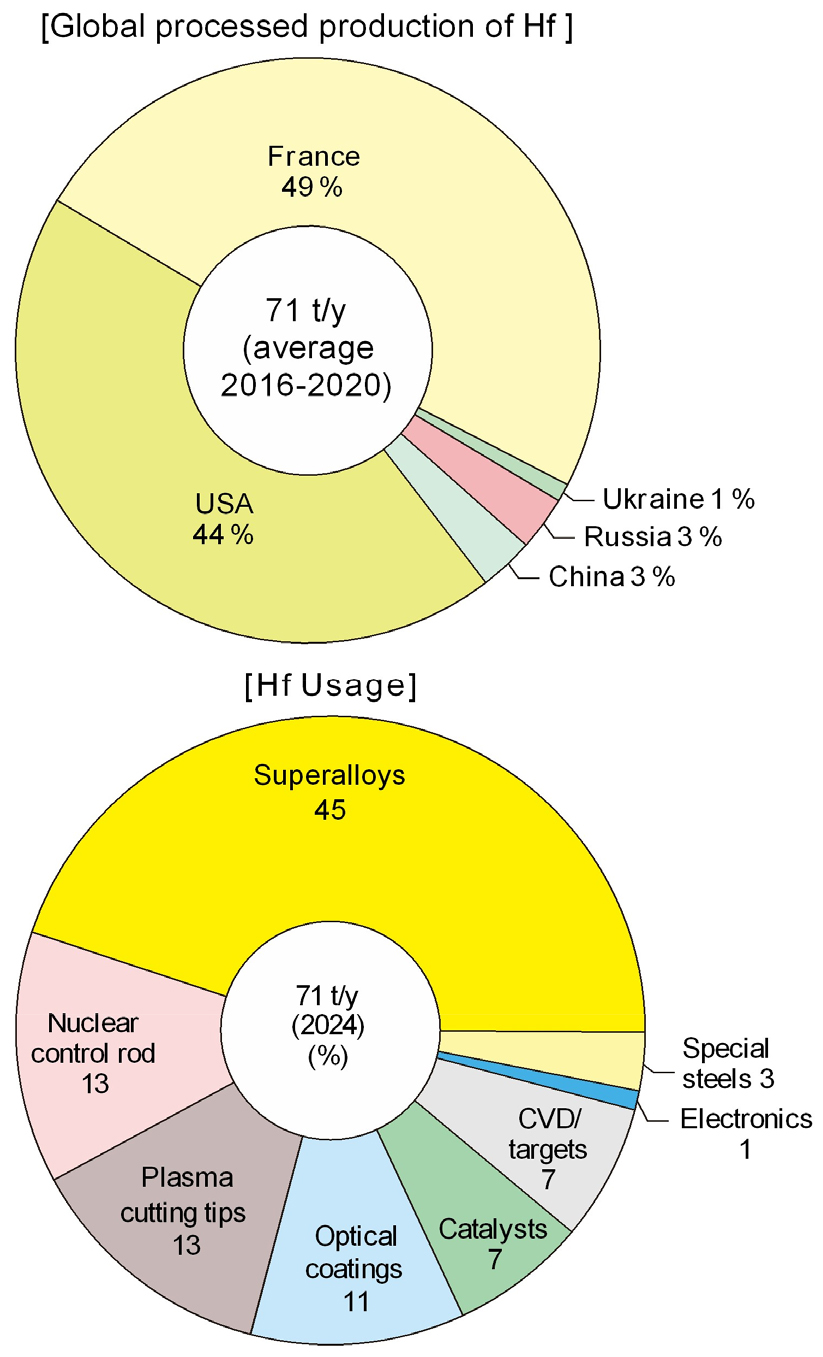
- Hafnium (Hf) is a rare metal that is essential for advanced industries such as nuclear power, superalloys, and semiconductors. This paper reviews Hf production, utilization, and smelting technologies. The global annual production of Hf is only about 80 tons, with 45 % of metallic Hf used in Ni-based superalloys and 13 % used in control rods for nuclear reactor. Hafnium is recovered as a by-product in the production of high-purity metallic zirconium for the nuclear industry. Metallic Hf is produced either by molten salt electrolysis or by the Kroll process, which reduces hafnium tetrachloride (HfCl₄) with magnesium (Mg). High-purity Hf is produced from crude Hf through iodine refining, as well as via molten salt electrolysis and electron beam melting. Hf is used as an additive in superalloys and machining tools. However, the extent to which it is recycled is not well-known due its low contents in these materials, although. Hf used in superalloys is presumed to be recycled back into Ni-based alloys. In contrast, Hf used in control rods is stored as radioactive waste and therefore cannot be recycled. Waste targets used for semiconductors and machining chips are recycled through electron beam melting and refining. To recycle such hafnium scrap, it is necessary to achieve economies of scale.
- COLLAPSE
하프늄은 원자력, 초합금, 반도체 등의 첨단산업에 필수적인 희소금속이다. 본 논문에서는 이러한 Hf의 생산량과 용도 및 제련 기술 등에 관하여 고찰하였다. Hf의 전 세계 연간 생산량은 약 80 톤에 불과하며, 금속 Hf의 45 %는 Ni계 초합금에, 13 %는 원자로의 제어봉에 사용되고 있다. 이러한 Hf은 원자력 산업용의 고순도 금속 Zr을 생산하는 과정에서 부산물로 회수하고 있다. 금속 Hf은 Hf 염화물(HfCl4)을 Mg으로 환원하는 Kroll법이나 용융염 전해법으로 제조하고 있다. 조금속 Hf은 아이오딘법, 융용염 전해정련, 전자빔 용융정제를 거쳐 고순도 Hf으로 정제된다. Hf은 초합금 및 기계 가공용 등의 용도로 사용되고 있으나 Hf의 함유량이 낮아 리사이클링 실태에 관하여 잘 알려져 있지 않다. 그러나 초합금으로 사용된 Hf은 다시 Ni계 합금으로 리사이클링되는 것으로 추정된다. 원자로의 제어봉으로 사용된 Hf은 방사성 폐기물로 저장되어 있으므로 리사이클링 대상이 되지 못하고 있다. 반도체용의 타깃이나 가공 과정에서 발생하는 칩 등은 전자빔 용융 및 정제를 통하여 리사이클링하고 있다. 이러한 Hf 스크랩의 리사이클링을 위해서는 규모의 경제성을 확보하는 것이 필요하다.
-
Smelting and Recycling of Hafnium
-
Article Review
-
Review on Rare Earth Permanent Magnet Recycling Technology
희토류 영구자석 재활용 기술 동향 연구
-
Dongsoo Kim, Jungshin Kang
김동수, 강정신
- Rare earth elements possess unique chemical, electrical, magnetic, and luminescent properties that can significantly enhance the performance of existing products even when …
희토류 원소들은 독특한 화학적, 전기적, 자성적, 발광적 성질로 인해 소량 첨가만으로 기존 제품의 성능을 월등하게 향상시키고, 상용화 가능한 대체재도 부재하여, 4차산업 및 …
- Rare earth elements possess unique chemical, electrical, magnetic, and luminescent properties that can significantly enhance the performance of existing products even when added in small amounts. Moreover, due to the absence of commercially viable substitutes, these elements hold high strategic value in the Fourth Industrial Revolution and advanced technology sectors. Each element exhibits distinct characteristics, enabling diverse applications of rare earth materials in fields such as smartphones, semiconductors, electric vehicle motors, wind turbines, precision-guided weapons, and other advanced equipment. Among these applications, permanent magnets account for the largest market share. South Korea relies on imports for the majority of neodymium permanent magnets, which are essential components used in electric vehicle production, robotics, consumer electronics and other related applications. However, research on recycling these materials remains insufficient. Therefore, this paper provides an overview and analysis of recent global issues surrounding the rare earth supply chain and current research trends in recycling technologies for rare earth permanent magnets.
- COLLAPSE
희토류 원소들은 독특한 화학적, 전기적, 자성적, 발광적 성질로 인해 소량 첨가만으로 기존 제품의 성능을 월등하게 향상시키고, 상용화 가능한 대체재도 부재하여, 4차산업 및 첨단산업에서 높은 전략적 가치를 가지고 있다. 각 원소마다 고유한 특성을 바탕으로 스마트폰, 반도체, 전기차 모터, 풍력 터빈, 정밀 유도 무기 및 첨단 장비 등 희토류 소재의 응용 분야가 매우 다양한데, 그 중 영구자석이 가장 큰 시장을 차지하고 있다. 한국은 전기차 생산부터 로봇, 가전제품까지 활용되는 가장 중요한 ‘네오디뮴 영구자석’의 대부분을 수입에 의존하고 있다. 하지만, 이에 대한 재활용 연구는 아직 미비한 실정으로, 본 논문에서 최근 희토류 공급망 글로벌 이슈와 희토류 영구자석의 재활용 기술에 대한 연구 동향을 개괄적으로 조사 및 분석하여 보았다.
-
Review on Rare Earth Permanent Magnet Recycling Technology
-
Research Paper
-
Preliminary Study on the Quantitative Analysis of Kaolinite based on Standard Mixed Samples
표준 혼합 시료 기반 카올리나이트 정량 분석 기초 연구
-
Nam-Il Kim, Jeong-Hoon Jo, Sang-Ser Goo, Yong-Seon Hwang
김남일, 조정훈, 구상서, 황용선
- Herein, we evaluated the accuracies and limitations of kaolinite quantification methods using standard mixtures of highly pure kaolinite and ISO standard sand. …
본 연구에서는 고순도 카올리나이트와 ISO 표준사를 혼합한 표준 시료를 대상으로, 카올리나이트 함량 정량을 위한 TG 및 XRD 분석(Rietveld 정량법)의 정확성과 한계를 비교·평가하였다. …
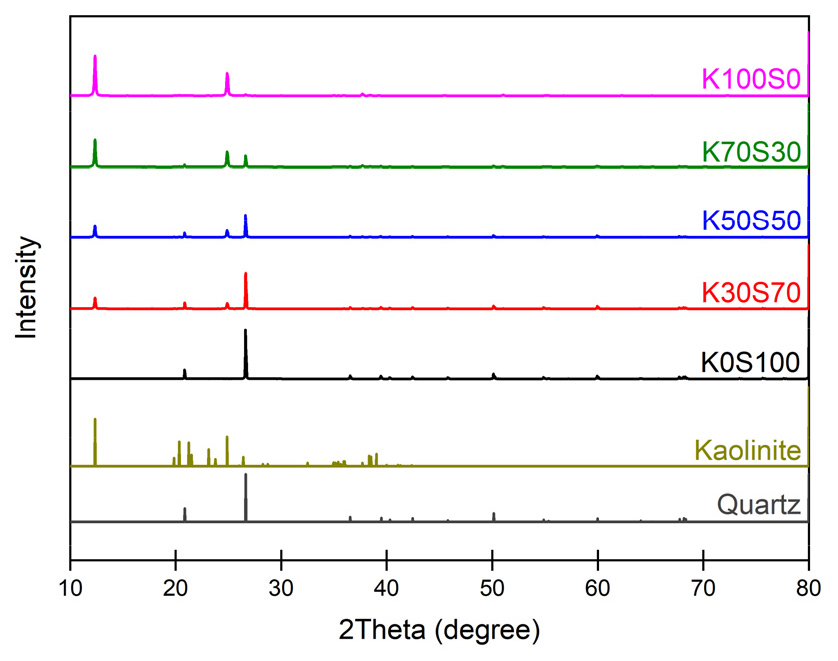
- Herein, we evaluated the accuracies and limitations of kaolinite quantification methods using standard mixtures of highly pure kaolinite and ISO standard sand. Samples were subjected to thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) and X-ray diffractometry (XRD) with Rietveld refinement. TGA exhibited the highest accuracy, with an average error of 8.72% in the 450–750 °C dehydroxylation range, which indicates that this temperature range is suitable for quantifying kaolinite. In contrast, XRD exhibited high accuracies for single-phase samples but showed a higher average error of 10.31% for mixed samples owing to peak overlap among minerals. These findings confirm that single-method approaches are of limited reliability when applied to complex mixtures or natural clays containing multiple mineral phases. Therefore, integrating complementary techniques such as Fourier-transform infrared and X-ray fluorescence spectroscopies is essential for enhancing reliability and consistency during kaolinite quantification using a multi-method analytical framework.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구에서는 고순도 카올리나이트와 ISO 표준사를 혼합한 표준 시료를 대상으로, 카올리나이트 함량 정량을 위한 TG 및 XRD 분석(Rietveld 정량법)의 정확성과 한계를 비교·평가하였다. TG 분석에서는 450–750℃의 탈수산화 온도 범위에서 평균 오차 8.72%로 가장 높은 정확도를 보였으며, 이는 카올리나이트 정량 분석에 적합한 온도 구간으로 판단된다. 반면, XRD 분석은 단일 성분 시료에서는 정확도가 높았으나 혼합 시료의 경우 광물 간 피크 중첩 현상으로 인해 평균 오차가 10.31%로 증가하는 한계를 나타냈다. 이로써 단일 분석 기법에 의존할 경우, 복합 시료나 천연 점토와 같이 다양한 광물이 공존하는 경우 정량 분석의 신뢰성이 낮아질 수 있음을 확인하였다. 따라서 FTIR, XRF 등의 다중 분석 기법을 병행하여 분석 결과를 상호 보완하는 통합적 접근이 필요하다.
-
Preliminary Study on the Quantitative Analysis of Kaolinite based on Standard Mixed Samples
-
Research Paper

-
A Study of Purification and Structural Recovery of Spent LIB Hydrometallurgical Leaching Residues via Water Leaching-Alkali Roasting
폐배터리 습식 제련 침출 잔사의 수침출-알칼리 배소 기반 정제 및 구조 회복에 관한 연구
-
Gihyun Kim, Nak-Kyoon Ahn, Kyungsoo Park
김기현, 안낙균, 박경수
- The rapid expansion of electric vehicles (EVs) and energy-storage systems (ESSs) has significantly increased the demand for lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) and has …
전기차(EV)와 에너지저장장치(ESS)의 보급 확대에 따라 리튬이온전지(LIB)의 수요가 급증히 증가하면서, 이에 따른 폐배터리 발생량 또한 빠르게 늘어나고 있다. LIB의 구성 성분 중 흑연은 …
- The rapid expansion of electric vehicles (EVs) and energy-storage systems (ESSs) has significantly increased the demand for lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) and has led to a sharp increase in the number of End-of-Life (EoL) batteries consequently. While graphite anode is an essential LIB component, accounting for approximately 12-21% of its weight, it is often consumed as a reductant during smelting or discarded as a leaching residue in current recycling processes, resulting in limited reuse. To address this issue, a two-step purification and regeneration process that combines water leaching and alkali roasting was suggested to recover graphite from the leaching residues in hydrometallurgical process for recycling EoL-LIBs. Sulfates of transition metals, such as Ni, Co, and Mn, were effectively removed through water leaching, while relatively stable Al species were retained. Insoluble impurities, such as Al2O3 and SiO2, were converted into soluble compounds, such as NaAlO2 and Na2SiO3, in the subsequent alkali-roasting step, which led to a reduction in the ash content of up to 44.5%. Some insoluble phases (e.g., NaAlSiO4) were also generated; hence, additional acid leaching treatment is expected to be beneficial. Moreover, structural analyses revealed that the interlayer spacing (d002) decreased from 0.3360 to 0.3346 nm, whereas the Raman D-band-to-G-band ratio (ID/IG) decreased from 0.53 to 0.34-0.37 during treatment. In addition, the C 1s XPS spectrum revealed that the relative intensity of the π-π* satellite peak increased from 5.0% to more than 9%, while the C=O peak disappeared, confirming that both graphite crystallinity and sp2 bonding domains were significantly restored. Taken together, these findings suggest that the alkali-roasting-based purification approach developed in this study effectively removes impurities while enhancing the structure and surface chemistry of graphite, with the regenerated graphite potentially usable as a LIB anode material.
- COLLAPSE
전기차(EV)와 에너지저장장치(ESS)의 보급 확대에 따라 리튬이온전지(LIB)의 수요가 급증히 증가하면서, 이에 따른 폐배터리 발생량 또한 빠르게 늘어나고 있다. LIB의 구성 성분 중 흑연은 약 12-21 wt%를 차지하는 핵심 소재임에도 불구하고, 재활용 공정에서는 대부분 제련 환원제로 사용되거나 침출 잔사 형태로 처리되어 활용도가 낮은 실정이다. 본 연구에서는 이러한 침출 잔사로부터 회수한 폐흑연을 대상으로 수침출과 알칼리 배소를 연계한 2단계 정제 및 재생 공정을 제안하였다. 수침출 단계에서는 전이금속 황산염(Ni, Co, Mn)이 효과적으로 제거된 반면, Al 성분은 상대적으로 안정적으로 잔류하였다. 이어서 수행한 알칼리 배소에서는 불용성 불순물(Al2O3, SiO2 등)이 NaAlO2, Na2SiO3 등의 수용성 화합물로 전환되어 회분(ash) 함량이 최대 44.5%까지 감소하였다. 다만, 일부 NaAlSiO4와 같은 수불용성상이 형성되어 추가적인 산침출 처리가 필요함을 확인하였다. 구조 분석 결과, 층간 간격(d002)은 0.3360 nm에서 0.3346 nm로 감소하였으며, Raman 분석에서 ID/IG 비가 0.53에서 0.34-0.37로 낮아졌다. 또한 XPS C 1s에서 π-π* 위성 피크가 5.0%에서 9% 이상으로 증가하고, C=O 피크가 소거되어 흑연의 결정성과 sp2 결합 영역이 뚜렷하게 회복된 것을 확인할 수 있었다. 이상의 결과를 종합하면, 본 연구에서 제안한 알칼리 배소 기반 정제 전략은 불순물 제거, 결정성 회복, 표면 화학 제어를 동시에 달성할 수 있음을 입증하였으며, 경제성 있는 재생 흑연의 LIB 음극재 활용 가능성을 제시한다.
-
A Study of Purification and Structural Recovery of Spent LIB Hydrometallurgical Leaching Residues via Water Leaching-Alkali Roasting
-
Research Paper
-
Influence of Controlled Cooling Rates on Clinker Microstructure and Phase Evolution with Machine Learning-Based Compressive Strength Prediction
제어된 냉각 속도가 클링커 미세구조와 상 진화에 미치는 영향 및 머신러닝 기반 압축강도 예측
-
Bilguun Mend, Youngjun Lee, Yong-Sik Chu
Bilguun Mend, 이영준, 추용식
- The effect of cooling rate on Portland cement clinker was studied using six regimes (2–100 °C/min) after sintering at 1450 °C. X-ray …
본 연구는 1450 °C에서 소성된 포틀랜드 시멘트 클링커의 상 변화, 미세구조, 그리고 압축강도에 미치는 영향을 평가하기 위해 2–100 °C/분 범위의 제어된 냉각 …
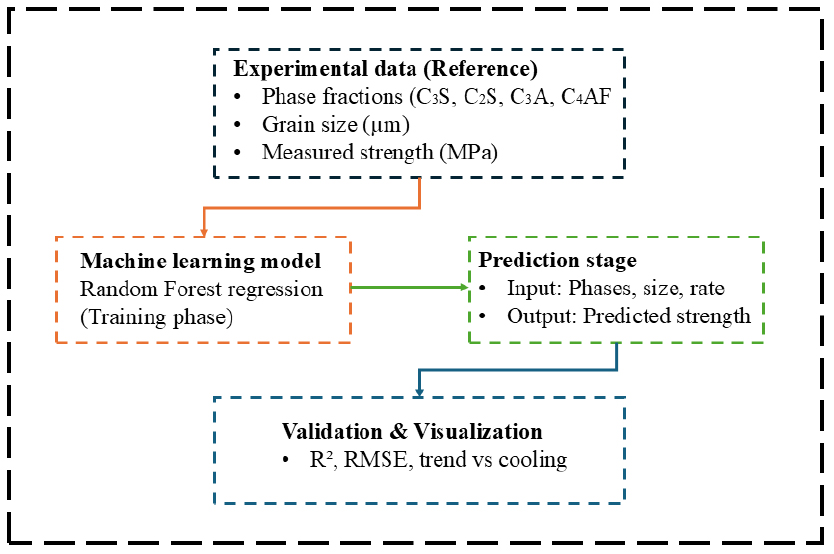
- The effect of cooling rate on Portland cement clinker was studied using six regimes (2–100 °C/min) after sintering at 1450 °C. X-ray diffraction rietveld refinement and optical analyses revealed that slow cooling stabilized monoclinic-C3S and β-C2S, while rapid quenching produced triclinic-C3S and γ-C2S, thereby reducing reactivity. A random forest model was used to predict compressive strength (R2 = 0.92) based on phase and microstructure data. Moderate cooling (20–50 °C/min) resulted in optimal strength and phase stability. The results indicate that controlled cooling governs clinker reactivity and data driven modeling enables reliable prediction of mechanical performance for sustainable, high-efficiency cement production.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구는 1450 °C에서 소성된 포틀랜드 시멘트 클링커의 상 변화, 미세구조, 그리고 압축강도에 미치는 영향을 평가하기 위해 2–100 °C/분 범위의 제어된 냉각 속도를 적용하여 그 효과를 분석하였다. XRD–Rietveld 분석과 광학현미경 관찰 결과, 느린 냉각에서는 단사정 C3S와 β-C2S가 안정화된 반면, 빠른 냉각에서는 삼사정 C3S와 γ-C2S가 형성되어 수경성이 저하되는 것으로 나타났다. 정량적 상 조성 정보와 결정립 크기 데이터를 기반으로 Random Forest 모델을 구축하여 클링커의 압축강도를 예측하였다. 중간 수준의 냉각 속도(20–50 °C/분)에서는 상 안정성, 미세조직의 균질성, 강도 발현이 가장 우수한 것으로 확인되었다. 이러한 결과는 냉각 공정의 정밀 제어가 클링커의 반응성을 좌우하는 핵심 요소임을 보여주며, 데이터 기반 모델링이 기계적 성능을 최적화하고 고효율·지속가능한 시멘트 생산을 지원하는 신뢰할 수 있는 도구임을 입증한다.
-
Influence of Controlled Cooling Rates on Clinker Microstructure and Phase Evolution with Machine Learning-Based Compressive Strength Prediction
-
Research Paper
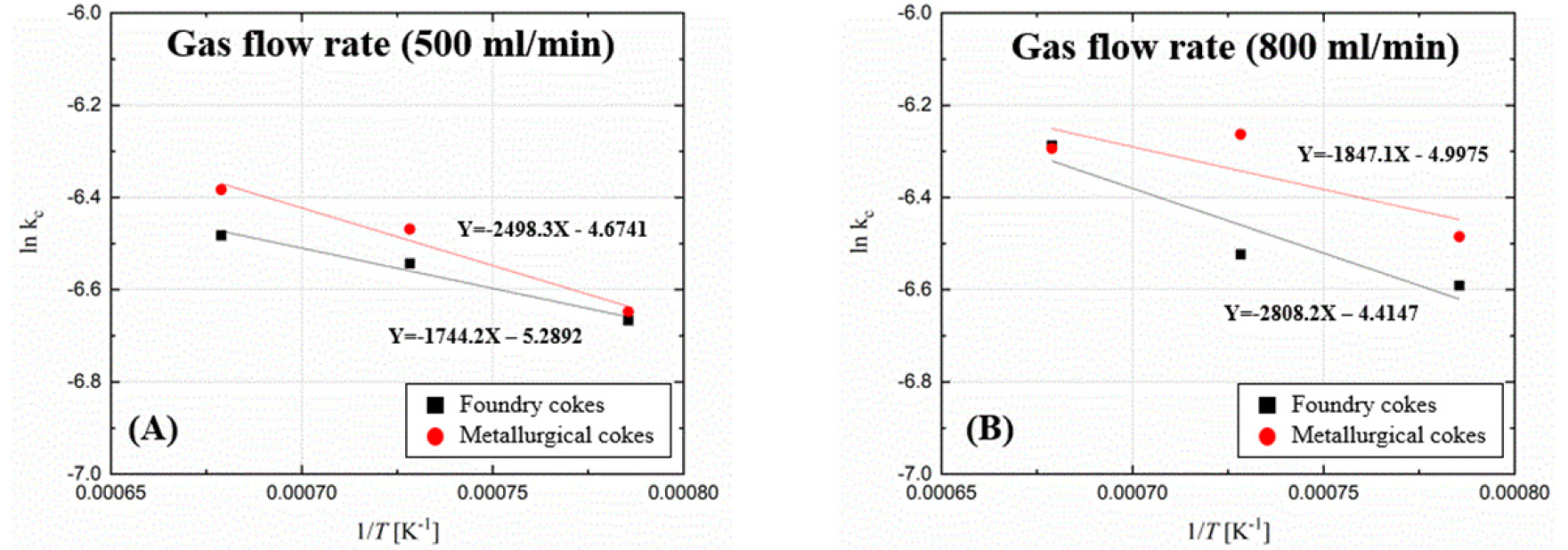
-
Combustion Behavior of Foundry and Metallurgical Cokes to Diversify Solid Fuel in Cupola for Mineral Wool Production
미네랄울 제조용 큐폴라로의 고체연료 다각화를 위한 주물용 및 야금용 코크스의 연소 거동
-
Sun-Joong Kim
김선중
- The transition to a sustainable circular economy necessitates the high-value utilization of slag, with slag wool production emerging as a promising approach. …
지속적인 자원순환 사회 실현을 위해 철강산업 부산물중 슬래그의 고부가가치 활용법으로 슬래그울 제조 연구가 필요하다. 본 연구에서는 주물용 및 야금용 코크스의 연소 거동을 …
- The transition to a sustainable circular economy necessitates the high-value utilization of slag, with slag wool production emerging as a promising approach. This study investigated the combustion behavior of foundry and metallurgical cokes and derived their combustion rate constants as foundational data for modeling temperature distribution inside a cupola furnace. Combustion experiments were conducted at 1273, 1373, and 1473 K, by first purging with N₂ gas at room temperature, followed by thermogravimetric analysis under dried air flows of 500 and 800 ml/min; post-combustion residues were characterized through X-ray diffraction. The combustion rates of both cokes accelerated with an increase in temperature and oxygen flow; the metallurgical coke exhibited higher reactivity, while the foundry coke possessed a higher calorific value. These findings indicate that foundry coke is a suitable heat source for the cupola. The residues mainly comprised SiO2 and Al2O3, with minor phases such as Fe2O3 and CaO. Based on kinetic data, combustion rate constants (kc) were derived as Arrhenius-type functions of temperature for each flow condition, providing key parameters for developing an internal temperature distribution model for the cupola.
- COLLAPSE
지속적인 자원순환 사회 실현을 위해 철강산업 부산물중 슬래그의 고부가가치 활용법으로 슬래그울 제조 연구가 필요하다. 본 연구에서는 주물용 및 야금용 코크스의 연소 거동을 조사하고 연소속도 상수를 도출하여 큐폴라 내부 온도를 예측하기 위한 모델의 기초 연구에 해당한다. 연소 실험은 상온에서 N₂가스로 분위기 치환후 1273, 1373, 1473K 조건에서 Dried Air (500, 800 ml/min) 분위기에서 열중량분석법으로 분석하고, 연소 후 회수된 회분상을 XRD로 확인하였다. 실험 결과 온도 및 산소 유량 증가에 따라 두 코크스 모두 연소속도가 증가하였으며, 야금용 코크스가 반응성이 우수하였으나 발열량은 주물용 코크스가 더 높아 큐폴라 용융로 열원으로서의 활용 가능성을 보였다. 회분은 주로 SiO2와 Al2O3로 구성되었고 Fe2O3와 CaO를 함유하는 상도 미량 포함하는 것으로 확인되었다. 또한 반응 속도 실험 데이터를 기반으로 유량 조건에 따라 각각의 연소속도 상수(kc)를 온도와의 관계식으로 도출하여 큐폴라 내부 온도 분포 모델 개발에 활용할 수 있는 기초 자료를 마련하였다.
-
Combustion Behavior of Foundry and Metallurgical Cokes to Diversify Solid Fuel in Cupola for Mineral Wool Production
-
Research Paper
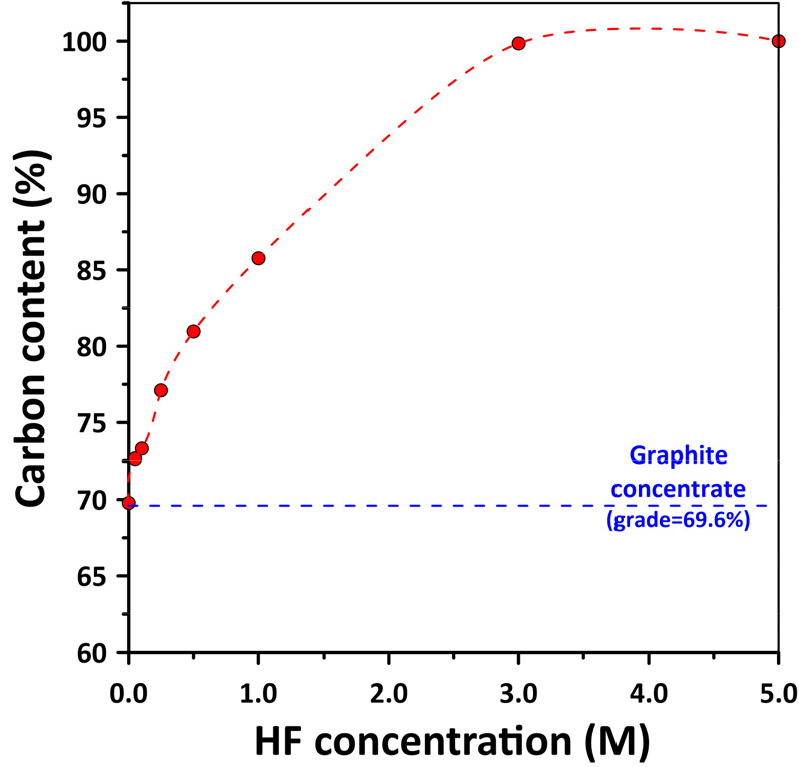
-
Experimental Study on Flotation-Chemical Purification for High-Purity Graphite Production from Domestic Natural Graphite Ore
국내 천연 흑연광의 고순도 흑연 생산을 위한 부유선별-화학적 정제에 대한 실험적 연구
-
Serin Kang, Jaemin Ahn, Donghyun Kim, Seongmin Kim, Seongsoo Han, Wonjae Lee, Seungwook Shin, Ki Min Roh, Haesung Jeong, Yosep Han
강세린, 안재민, 김동현, 김성민, 한성수, 이원재, 신승욱, 노기민, 정해성, 한요셉
- This study investigated the production of high-purity graphite from natural graphite ore collected in Geumam, Dangjin, Korea. The ore was processed using …
본 연구는 충청남도 당진시 금암 지역에서 채취한 천연 흑연광을 대상으로 부유선별과 황산-불산을 활용한 화학적 정제 공정으로부터 고순도 흑연 제조 가능성을 실험적으로 검토하였다. …
- This study investigated the production of high-purity graphite from natural graphite ore collected in Geumam, Dangjin, Korea. The ore was processed using a combined flotation and acid purification process involving sulfuric acid (H2SO4) and hydrofluoric acid (HF). A conventional, multi-stage flotation process yielded a graphite concentrate with an approximate grade of 70 %. Purification experiments were then conducted under various H2SO4 (0.05-5.0 M) and HF (0.05-5.0 M) concentrations to evaluate their effect on purification performance. The results showed that H2SO4 treatment alone had little effect on enhancing the purity, whereas carbon content significantly increased with higher concentrations of HF, achieving over 99.9 % purity at a concentration of 5.0 M. SEM-EDS analysis confirmed that silicon (Si), aluminum (Al), and iron (Fe) impurities were almost completely removed under high-HF conditions. Particle size analysis revealed a more uniform distribution after chemical purification. These findings suggest that HF plays a dominant role in impurity removal from SiO2-rich siliceous graphite ores compared to H2SO4.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구는 충청남도 당진시 금암 지역에서 채취한 천연 흑연광을 대상으로 부유선별과 황산-불산을 활용한 화학적 정제 공정으로부터 고순도 흑연 제조 가능성을 실험적으로 검토하였다. 다단 부유선별 공정을 적용한 결과, 총 탄소 함량 70 wt.%의 정광을 얻었다. 이후, 화학적 정제를 통하여 고순도 흑연 생산 특성을 평가하기 위해 황산과 불산의 다양한 농도로 설정하여 실험을 수행하였다. 이에 황산(0.05-5.0 M) 및 불산(0.05-5.0 M) 농도를 변화시켜 정제 거동을 비교한 결과, 황산 단독 처리에서는 순도 향상이 거의 없었으나, 불산 농도가 증가함에 따라 탄소 함량이 급격히 상승하였고 5.0 M HF 조건에서 99.9 % 이상의 고순도 흑연을 얻을 수 있었다. SEM–EDS 분석 결과, 고농도 HF 처리 시 Si, Al, Fe 성분 등이 제거되었으며, 입도분석에서도 화학 정제 후 입자 크기가 균일해지는 경향을 나타내었다. 이러한 결과는 SiO2 함량이 높은 규산염계 흑연광의 특성으로 인해 황산보다 불산이 정제에 미치는 효과가 더 큰 것으로 파악된다.
-
Experimental Study on Flotation-Chemical Purification for High-Purity Graphite Production from Domestic Natural Graphite Ore
-
Research Paper
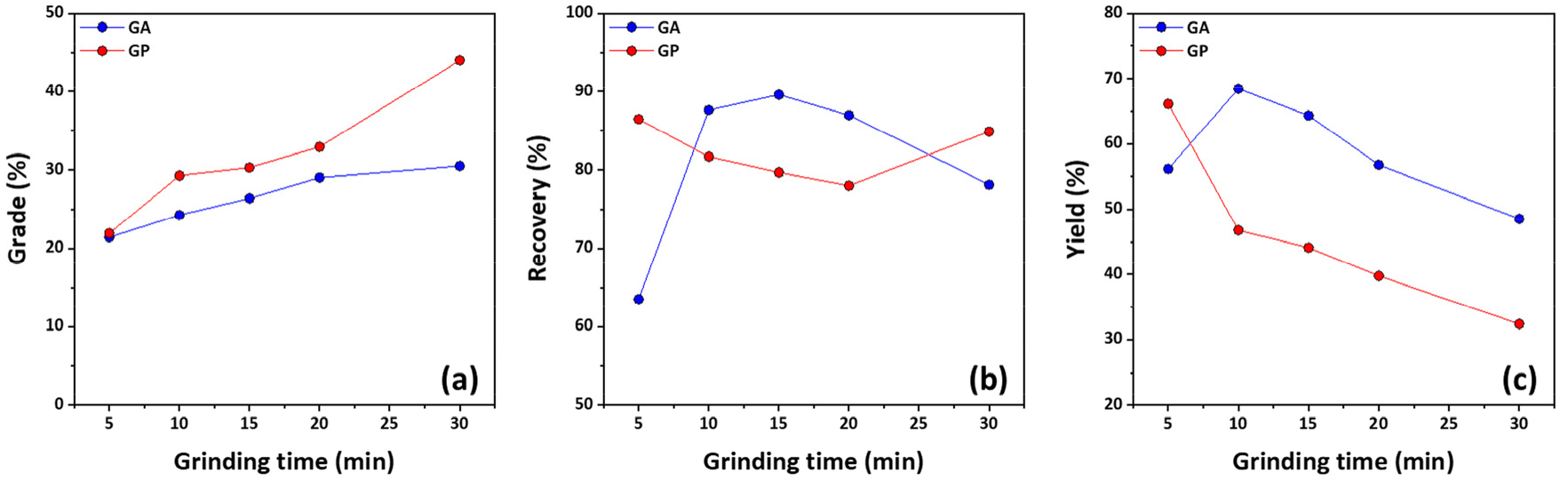
-
Influence of Mineral Composition on Grinding Behavior and Flotation Performance of Low-Grade Domestic Graphite Ore
국내 저품위 흑연광의 광물 조성에 따른 분쇄 거동 및 부유선별 성능의 영향
-
Donghyun Kim, Jaemin Ahn, Sunghyun Bae, Serin Kang, Seongsoo Han, Wonjae Lee, Seongmin Kim, Ki Min Roh, Seungwook Shin, Yosep Han
김동현, 안재민, 배성현, 강세린, 한성수, 이원재, 김성민, 노기민, 신승욱, 한요셉
- In this study, the mineralogical characteristics, grinding efficiency, and flotation of two low-grade natural graphite ores from different domestic regions (GA and …
본 연구에서는 국내 다른 두 지역 저품위 흑연광을 대상으로 광물학적 특성, 분쇄 및 부유선별 특성을 비교하였다. 두 지역 금암 (GA)와 가평 (GP) …
- In this study, the mineralogical characteristics, grinding efficiency, and flotation of two low-grade natural graphite ores from different domestic regions (GA and GP) were the subject of a comparative investigation. Despite the similarity in total carbon content between the GA (19.35 %) and GP (17.17 %) graphite, the results of XRF and XRD analyses demonstrated significant disparities in oxide and mineral compositions. The mineral assemblages present in the GA graphite were dominated by quartz and muscovite, while in the GP graphite, quartz and epidote were predominant. This indicates clear variations in the mineral composition present in the two graphite ores. SEM-EDS analysis revealed that the graphite crystals present in the GA graphite exhibited a generally larger size when compared to those found in the GP graphite. The rod-mill grinding test demonstrated that as grinding time increased, the particle size decreased for both graphite ores; however, the GA graphite exhibited coarse particle sizes under identical grinding conditions. The Bond Work Index (BWI) values of GA (13.25 kWh/t) and GP (11.15 kWh/t) confirmed the higher grinding resistance of the GA graphite, consistent with the rod-mill results. In flotation experiments, the GA graphite demonstrated optimal performance at 15 minutes of grinding, exhibiting a grade of 26.42 % and a recovery of 89.61 %. In contrast, the GP graphite attained its maximum performance at 30 minutes, achieving a grade of 43.99 % and a recovery of 84.87 %. The findings indicate that the difference in flotation performance between the two graphite ores is primarily governed by mineral composition, rather than carbon content. It is recommended that future research efforts concentrate on the optimization of flotation reagent conditions, including depressants, frothers, and collectors. These conditions should be based on the particular mineral characteristics of the gangue, with the objective of achieving maximum recovery of high-grade graphite.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구에서는 국내 다른 두 지역 저품위 흑연광을 대상으로 광물학적 특성, 분쇄 및 부유선별 특성을 비교하였다. 두 지역 금암 (GA)와 가평 (GP) 흑연광의 총 탄소함량 (GA 19.35 %, GP 17.17 %)은 비슷하였으나, XRF 및 XRD 분석 결과 산화물 함량과 광물 조성에서 뚜렷한 차이를 보였다. GA 흑연광은 석영과 백운모가, GP 흑연광은 석영과 녹렴석이 우세하게 존재하여 서로 다른 광물 조성이 나타났다. SEM-EDS를 통한 흑연 결정크기를 분석한 결과, GA 흑연광이 GP 흑연광 보다 결정크기가 큰 것을 확인하였다. 두 시료 모두 분쇄시간이 증가함에 따라 입도가 감소하였으나, 동일한 분쇄 조건에서 GA 흑연광이 GP 흑연광보다 상대적으로 입도가 큰 것을 확인하였다. 또한, GA 및 GP의 분쇄일지수는 각각 13.25 kWh/t 그리고 11.15 kWh/t로 확인되었다. 부유선별 결과, GA 흑연광은 분쇄 시간 15분에서 정광 품위 26.42 %, 회수율 89.61 %로 최적 조건을 보였으며, GP 흑연광은 30분에서 품위 43.99 %, 회수율 84.87 %로 최적 조건을 보였다. 이러한 결과로 두 지역 흑연광의 선광 성능 차이가 탄소 함량보다 광물 조성차이에 의한 분쇄 후 입도 분포의 차이가 영향을 미치는 것으로 확인되었다. 향후 연구에서는 각 흑연광을 구성하는 맥석 광물의 특성에 따라 억제제, 기포제 및 포수제 등의 시약 조건을 최적화하여 고품위 흑연 회수를 극대화할 수 있는 부유선별 공정 개발이 필요할 것으로 사료된다.
-
Influence of Mineral Composition on Grinding Behavior and Flotation Performance of Low-Grade Domestic Graphite Ore
-
Research Paper
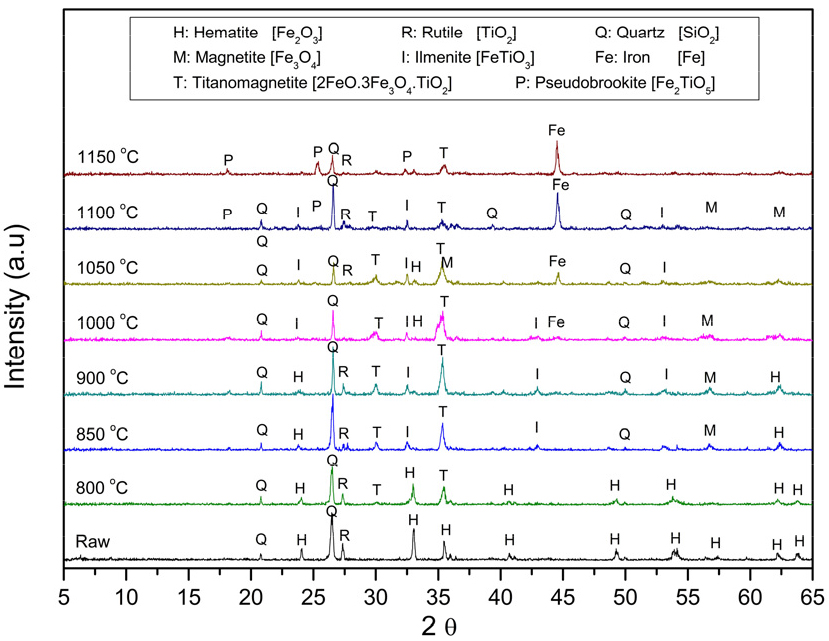
-
Magnetizing Roasting Characteristics to Enhance the Magnetic Separation Efficiency of Titanium Ore from the Taebaek Myeon-san Layer Titanium Deposit
태백 면산층 타이타늄 광석의 자력선별 효율 향상을 위한 자화배소 특성 연구
-
Fausto Moscoso Pinto, Seongho Lee, Hyung-Seok Kim
모스코소 핀토 파우스토, 이성호, 김형석
- This study aimed to enhance the grade and yield of titanium oxide through magnetic separation of titanium ore from the Taebaek Myeon-San …
본 연구는 비자성인 금홍석을 함유한 태백지역 면산층 타이타늄 광석으로부터 자력선별에 의해 산화티탄의 품위 및 실수율을 향상시키는 목적으로 타이타늄 광석의 자화배소(Magnetizing roasting) 및 …
- This study aimed to enhance the grade and yield of titanium oxide through magnetic separation of titanium ore from the Taebaek Myeon-San Layer titanium deposit, which contains non-magnetic rutile. The magnetizing roasting characteristics of the ore and the magnetic separation properties of the roasted product were investigated. The titanium ore in the Myeon-San Layer deposit is a sedimentary rock in which the target mineral, rutile (TiO2), is intergrown with hematite (Fe2O3) and gangue minerals, including quartz (SiO2) and clay minerals. Consequently, there are limitations to improving the grade and yield of titanium oxide using conventional beneficiation methods. When graphite, a reducing agent, was added to the titanium ore at levels of 10-30 % and the mixture was roasted at temperatures between 900 and 1,100 °C, the rutile reacts with hematite in the 925 to 975 °C range, transforming them into titanomagnetite (a solid solution of Fe2TiO3 and Fe3O4), a weakly magnetic mineral, and ilmenite (FeTiO3), a paramagnetic mineral. The excess hematite was reduced to magnetite (Fe3O4), a ferromagnetic mineral. However, at temperatures above 1,000 °C, these minerals were reduced again to rutile and metallic iron (Fe). Magnetic separation during synthesis indicated that rutile was not recovered because it is nonmagnetic. Nevertheless, magnetite was recovered at over 90 % using a magnetic field of 0.1 T, titanomagnetite at 1.0 T, and ilmenite at 1.2 T, confirming that titanomagnetite and ilmenite, as roasted products, exhibit high magnetic sensitivity. During magnetic separation at 0.8 T for products roasted at 900-1,050 °C, titanomagnetite and ilmenite, which are titanium-bearing minerals, were recovered as magnetic concentrates. Therefore, when titanium ore from the Myeon-San Layer deposit is mixed with a reducing agent, roasted, and separated by magnetic separation, the non-magnetic rutile reacts with hematite to form titanomagnetite and ilmenite with high magnetic sensitivity. This demonstrates that the yield of titanium oxide can be increased.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구는 비자성인 금홍석을 함유한 태백지역 면산층 타이타늄 광석으로부터 자력선별에 의해 산화티탄의 품위 및 실수율을 향상시키는 목적으로 타이타늄 광석의 자화배소(Magnetizing roasting) 및 자화배소 산물의 자력선별 특성을 알아보았다. 왜냐하면 면산층 타이타늄 원광은 목적광물인 금홍석(TiO2)이 수반광물인 적철석(Fe2O3), 그리고 맥석광물인 석영(SiO2) 및 점토광물 등이 미세한 입자로 혼합된 퇴적암이기 때문에 전통적인 선광방법으로는 산화티탄 성분의 품위 및 실수율을 향상시키는데 한계성이 있기 때문이다. 타이타늄 광석에 환원제인 흑연을 10~30 % 범위로 혼합하여 900~1,100 °C의 온도범위에서 자화배소한 결과, 925~975 °C의 온도범위에서 타이타늄 광석 내 금홍석은 적철석과 상호반응하여 약자성체인 티타노마그네타이트(Titanomagnetite; Fe2TiO3와 Fe3O4의 고용체)와 상자성체인 티탄철석(ilmenite; FeTiO3)으로 변질되었고, 잉여의 적철석은 강자성체인 자철석(Magnetite; Fe3O4)로 환원되었다. 그러나 1,000 °C 이상에서 이들 광물은 다시 금홍석과 금속철(Metallic Fe)로 환원되었다. 자화배소 산물들을 합성하여 자력선별한 결과, 금홍석은 자력감응도가 전혀 없어 회수되지 않지만, 자철석은 0.1 T 이상에서 티타노마그네타이트는 1.0 T 이상에서 티탄철석은 1.2 T 이상에서 90 % 이상 회수되어 자화배소 산물인 티타노마그네타이트 및 티탄철석의 자력감응도는 높은 것으로 확인되었다. 면산층 타이타늄 광석을 900~1,050 °C의 온도범위에서 자화배소한 결과, 함 티탄광물인 티타노마그네타이트와 티탄철석이 생성되었고, 이들 자화배소 산물을 0.8 T로 자력선별한 결과, 티타노마그네타이트와 티탄철석이 자선정광으로 효율적으로 회수되었다. 따라서 면산층 타이타늄 광석에 환원제를 혼합하여 자화배소하면 광석 내 비자성의 금홍석이 적철석과 반응하여 자력감응도가 높은 티타노마그네타이트와 티탄철석으로 변질되기 때문에 자력선별만으로 산화티탄의 품위 및 실수율을 향상시킬 수 있는 가능성을 확인할 수 있었다.
-
Magnetizing Roasting Characteristics to Enhance the Magnetic Separation Efficiency of Titanium Ore from the Taebaek Myeon-san Layer Titanium Deposit



 Resources Recycling
Resources Recycling








